Current Needs
More Information
Picture Archive Communication System (PACS)
PACS is a medical imaging technology used by healthcare organizations to securely store, transmit, and share electronic images and reports. PACS is a critical tool for patient care, used locally and abroad to make informed patient treatment decisions. Using PACS, physicians and specialists from other hospital sites are able to instantly access images (x-Ray’s, CT scans, ultrasounds, etc.) from any of SBGHC’s hospital sites in Chesley, Durham, Kincardine and Walkerton. A regional PACS system is significant when patients travel to other hospitals for healthcare, as access to prior imaging is readily available.
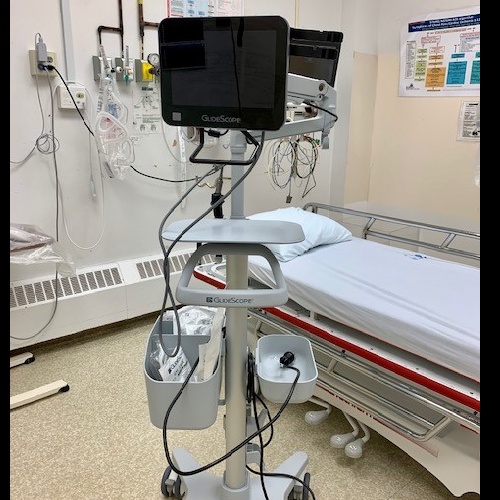
Glidescope
Intubation can be difficult for many reasons and a Glidescope provides an electronic visual of the patient’s airway, which is a better view than that of a direct laryngoscope.
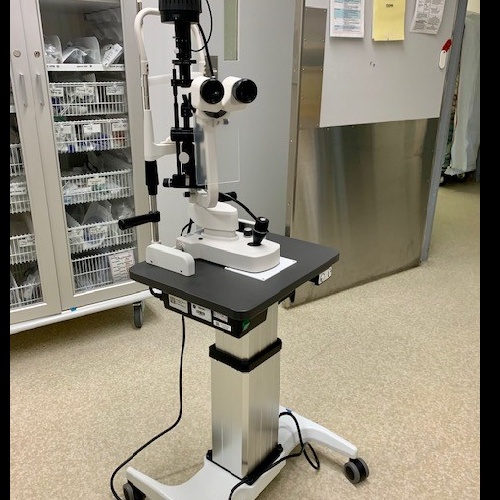
ER Slit Lamp
A slit lamp exam can help diagnose the following conditions: macular degeneration, a chronic condition affecting the part of the eye that is responsible for central vision. detached retina, a condition when the retina, which is an important layer of tissue at the back of the eye, becomes detached from its base.
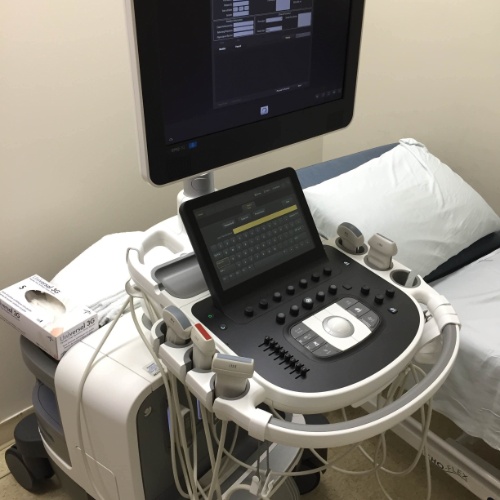
Ultrasound Machine
Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves to produce pictures of the inside of the body. It is used to help diagnose the causes of pain, swelling and infection in the body's internal organs and to examine a baby in pregnant women and the brain and hips in infants. It's also used to help guide biopsies, diagnose heart conditions, and assess damage after a heart attack. Ultrasound is safe, noninvasive, and does not use ionizing radiation.
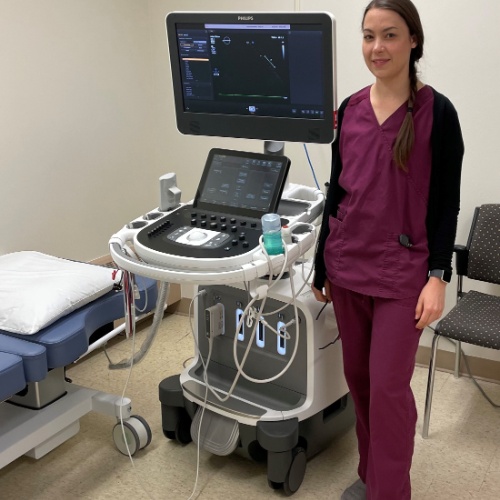
Ultrasound Machine for Echocardiography
Since 2017, a team of four General and Subspecialty Cardiologists, with expertise in Electrophysiology, Interventional Cardiology and Heart Failure, have been conducting clinics on a weekly basis in Kincardine making the site a referral centre for cardiology and echocardiography.
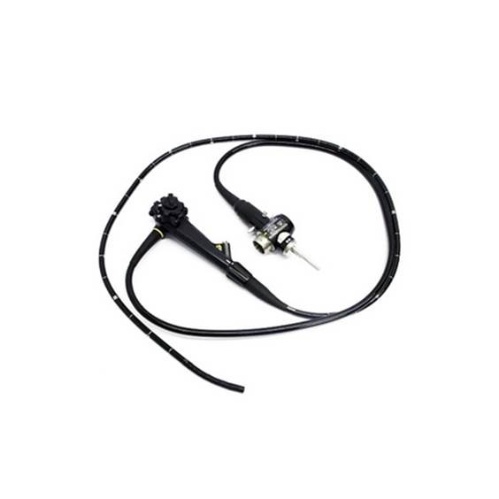
Pediatric Colonscope
A Pediatric colonscope allows more flexibility and reduces risks.
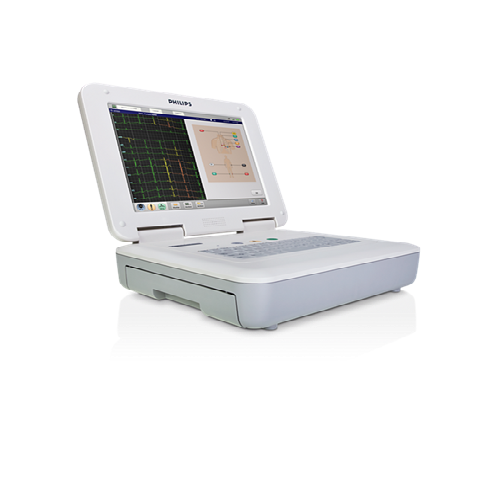
Philips Cardiograph and Bedside Monitoring
Philips Cardiograph is designed to simplify diagnostic ECG testing and streamline workflow allowing a quicker response time for patient results to be seen.
Powerful bedside monitoring supplying comprehensive patient information at a glance, it can make a real difference when multiple patients and priorities need attention.
Panic Alarm
Staff and patient safety is a priority for SBGHC. An updated panic alarm will provide a speedy response to the staff or patient in need.
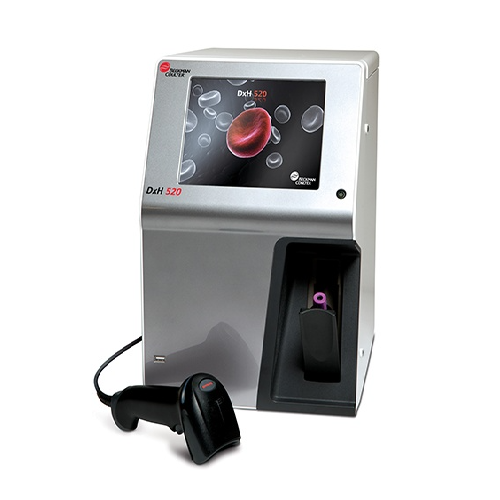
Hematology Analyzer
Provides a 5 part white blood cell differential, hemoglobin levels.
Blood Bank Fridge
Used to store packed red blood cells and other blood products for transfusion.